class 10 ch light and reflection exercise....
We'll come to very helpful blog
Exercise of
Page No: 178
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1. Name the spherical mirror which has:
a) virtual principal axis
b) real principal axis
Answer:
a) Convex mirror
b) Concave mirror
Q2. Out of convex mirror and concave mirror, whose focus is situated behind the mirror?
Answer:
Convex mirror has its focus behind.
Q3. Find the focal length of a concave mirror whose radius of curvature is 32cm.
Answer:
Radius of curvature, R = 32cm
Focal length, f = ?
We know that,
f = R/2
f = 32/2 = 16cm
Q4. If the focal length of a convex mirror is 25cm, what is its radius of curvature?
Answer:
Focal length, f = 25cm
Radius of curvature, R = ?
We know that,
f = R/2
R = 2f
R = 50cm
Q5. Fill in the following blanks with suitable words:
a) Parallel rays of light are reflected by a concave mirror to a point called the ……..
b) The focal length of a concave mirror is the distance from the ……… to the mirror.
c) A concave mirror ….. rays of light whereas a convex mirror ……. rays of light.
d) For a concave mirror, parallel rays of light appear to diverge from a point called the ……
Answer:
a) Principal focus
b) Principle focus
c) Converges and diverges
d) Principle focus
Short Answer Type Questions
Q6. What is a spherical mirror? Distinguish between a concave mirror and a convex mirror.
Answer:
When the hollow sphere of glass as a reflecting surface, it is known as a spherical mirror. There are two types of spherical mirrors: concave mirror and convex mirror.
Difference between concave mirror and convex mirror:
a) A concave mirror has a bent surface from which the reflection of light takes place while a convex mirror has a bulged out surface from which the reflection of light takes place.
b) Concave mirrors converge the parallel rays of light while convex mirrors diverge the parallel rays of light.
Q7. Name the two types of spherical mirrors. What type of mirror is represented by the:
a) back side of a shining steel spoon?
b) front side of a shining steel spoon?
Answer:
Two types of spherical mirrors are concave mirror and convex mirror.
a) Convex mirror
b) Concave mirror
Q8. What is the relation between the focal length and radius of curvature of a spherical mirror? Calculate the focal length of a spherical mirror whose radius of curvature is 25cm.
Answer:
The relation between the focal length and the radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is:
f = R/2.
Given,
R = 25cm
f = ?
We know that, f = R/2
Therefore, f = 12.5cm
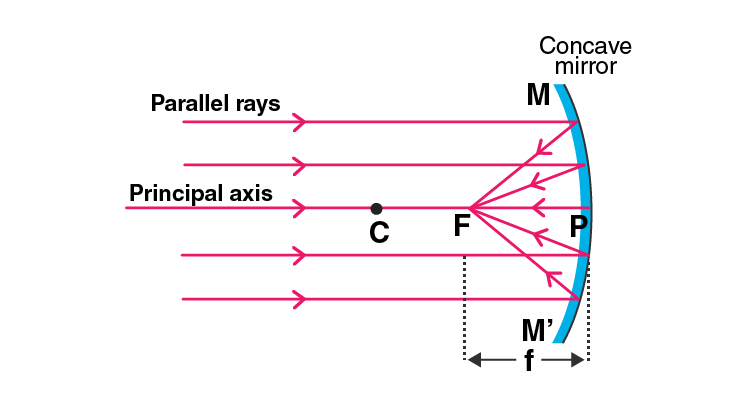
Q9. Explain with a suitable diagram, how a concave mirror converges a parallel beam of light rays. Mark clearly the pole, focus, and centre of curvature of concave mirror in this diagram.
Answer:
After reflection, all the parallel light rays converge at the principal focus as the concave mirror converges the parallel beam of light rays. This is the reason why it is known as converging mirror.

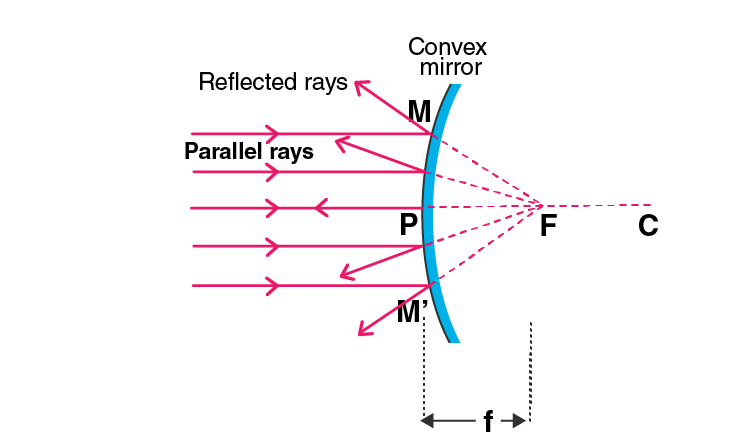
Q10. Describe with a suitable diagram, how a convex mirror diverges a parallel beam of light rays. Mark clearly the pole, focus, and the centre of curvature of convex mirror in this diagram.
Answer:
After the reflection, the light rays diverge from the principal focus and that is why convex mirror is also known as diverging mirror.
Long Answer Type Questions
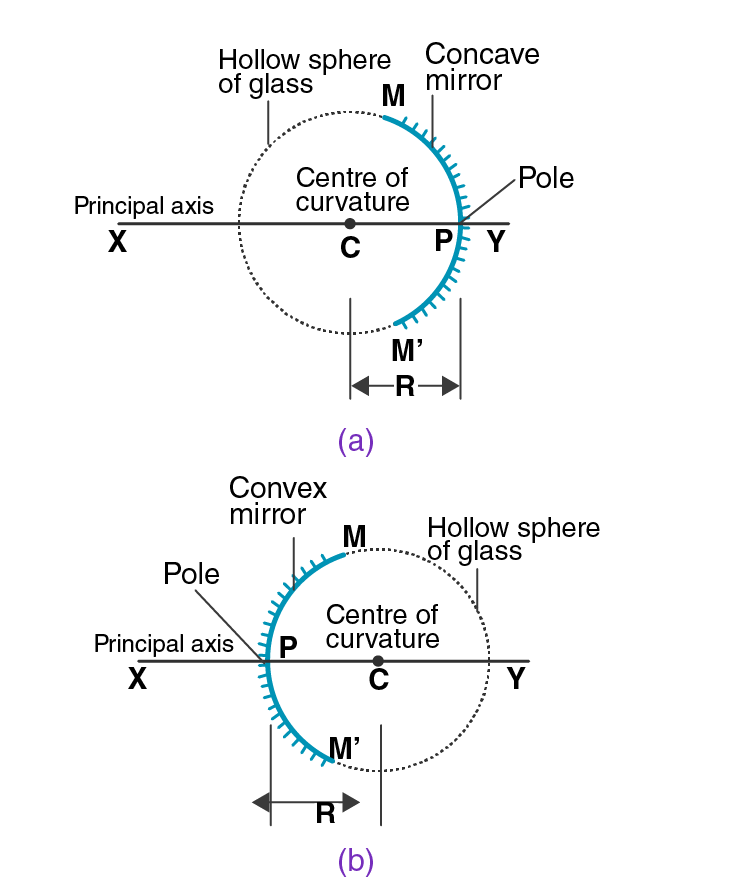
Q11. Define a) centre of curvature
b) radius of curvature
c) pole
d) principal axis
e) aperture of a spherical mirror with the help of a labelled diagram.
Answer:
a) Centre of curvature: It is the centre of the hollow sphere of glass of which a mirror is a part.
b) Radius of curvature: It is the radius of the hollow sphere of glass of which a mirror is a part.
c) Pole: The centre of the spherical mirror.
d) Principal axis: It is the straight line that passes through the centre of curvature and to the pole of the spherical mirror.
e) Aperture: The portion of a mirror from where the reflection of light takes place.
Q12. a) Define i) principal focus of a concave mirror
ii) focal length of a concave mirror
b) Draw diagram to represent the action of a concave mirror on a beam of parallel light rays. Mark on this diagram principal axis, focus F, centre of curvature C, pole P, and the focal length f of the concave mirror.
Answer:
a)
i) Principal focus of a concave mirror: The point on the principal axis on which all the light rays converge after reflection in a concave mirror.
ii) Focal length of a concave mirror: The distance between the pole and the principal axis is known as the focal length of a concave mirror.
b)
Q13. a) What is meant by i) principal focus of a convex mirror ii) focal length of a convex mirror?
b) Draw diagram to show the action of convex mirror on a beam of parallel light rays. Mark on this diagram principal axis, focus F, centre of curvature C, pole P, and focal length f of the convex mirror.
Answer:
a)
i) Principal focus of a convex mirror: When all the reflected light rays meet at a point after diverging in a convex mirror is known as principal focus of a convex mirror.
ii) Focal length of a convex mirror: The distance from the pole and the principal focus is known as the focal length of a convex mirror.
b)

Multiple Choice Questions
Q14. In a convex spherical mirror, reflection of light takes place at:
a) a flat surface
b) a bent-in surface
c) a bulging-out surface
d) an uneven surface
Answer:
The correct option is c) a bulging-out surface
Q15. A diverging mirror is:
a) a plane mirror
b) a convex mirror
c) a concave mirror
d) a shaving mirror
Answer:
The correct option is b) a convex mirror
Q16. If R is the radius of curvature of a spherical mirror and f is its focal length then:
a) R = f
b) R = 2f
c) R = f/2
d) R = 3f
Answer:
The correct option is b) R = 2f
Q17. The focal length of a spherical mirror of radius of curvature 30cm is:
a) 10cm
b) 15cm
c) 20cm
d) 30cm
Answer:
The correct option is b) 15cm
Q18. If the focal length of a spherical mirror is 12.5cm less cm, its radius of curvature will be:
a) 25cm
b) 15cm
c) 20cm
d) 35cm
Answer:
The correct option is a) 25cm..
Comments
Post a Comment