class 10 ch light and reflection.. exercise..
Wellcome to very helpful blog
Exercise of chapter light and reflection..
Page No: 189
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1. For what position of an object, a concave mirror forms a real image equal in size to the object?
Answer:
At the centre of curvature
Q2. Where should an object be placed in front of the concave mirror so as to obtain its virtual, erect, and magnified image?
Answer:
The object should be placed between the pole and the focus.
Q3. For which positions of the object does a concave mirror produce an inverted, magnified, and real image?
Answer:
When the object is placed between the focus and the centre of curvature.
Q4. If an object is placed at the focus of a concave mirror, where is the image formed?
Answer:
The image is obtained at infinity.
Q5. If an object is at infinity in front of a concave mirror, where is the image formed?
Answer:
The image is formed at the focus.
Q6. For what position of an object, a real and diminished image is formed by a concave mirror?
Answer:
When the object is beyond the centre of curvature.
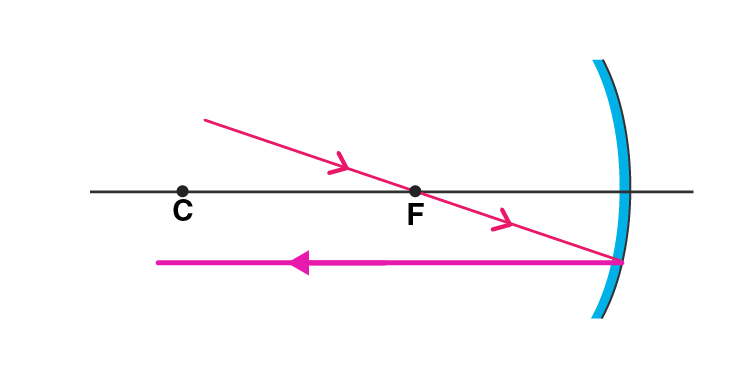
Q7. Copy this figure in your answer book and show the direction of the light ray after reflection:

Answer:
Following is the direction of the light ray after reflection:
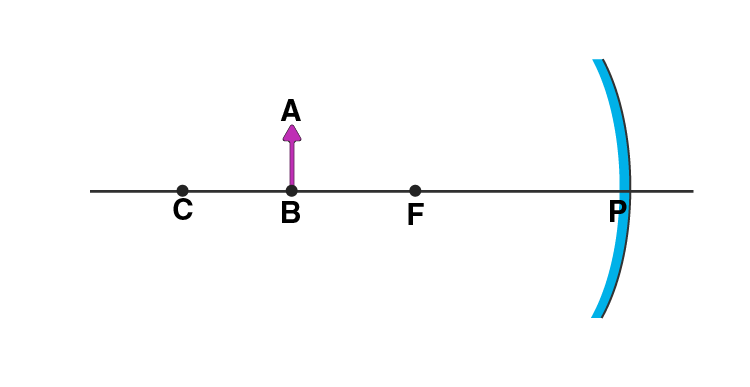
Q8. Draw the following diagram in your answer book and show the formation of image of the object AB.
Answer:
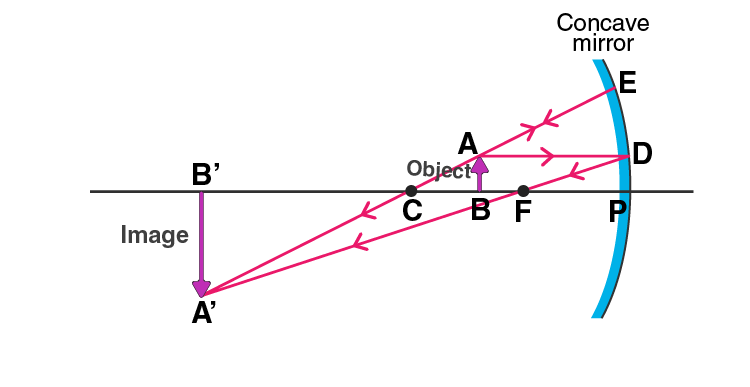
Q9. Draw the following diagram in your answer book and show the formation of image with the help of suitable rays.

Answer:
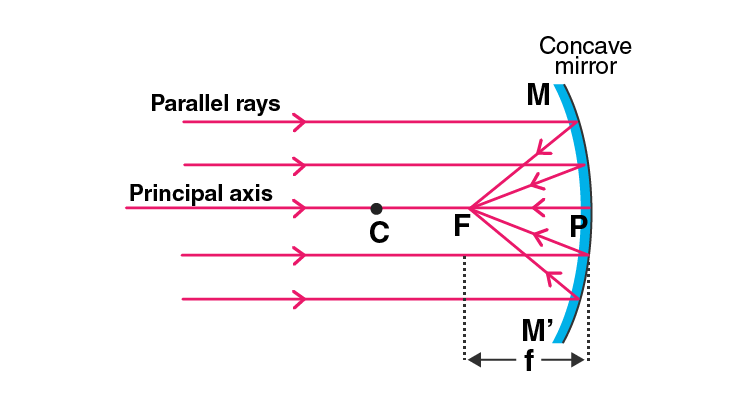
Q10. Which type of mirror could be used as a dentist’s mirror?
Answer:
A concave mirror can be used as a dentist mirror.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q11. Which kind of mirror is used in the headlights of a car? Why is it used for this purpose?
Answer:
Concave mirror is used in the headlights of a car. Concave mirror is used because when the light bulb is placed at the focus of a concave mirror reflector, the light rays diverge and gets collected by the concave reflector which is then reflected back as strong and parallel-sided beam of light.
Q12. Explain why a ray of light passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror gets reflected back along the same path.
Answer:
A ray of light passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror gets reflected back along the same path because the angle between the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection are at 0 degrees as the light rays strike the surface at right angle.
Q13. What is the minimum number of rays required for locating the image formed by a concave mirror for an object? Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a virtual image by a concave mirror.
Answer:
For locating the image formed by a concave mirror, minimum two rays are required. Following is the ray diagram for the formation of a virtual image by a concave mirror:
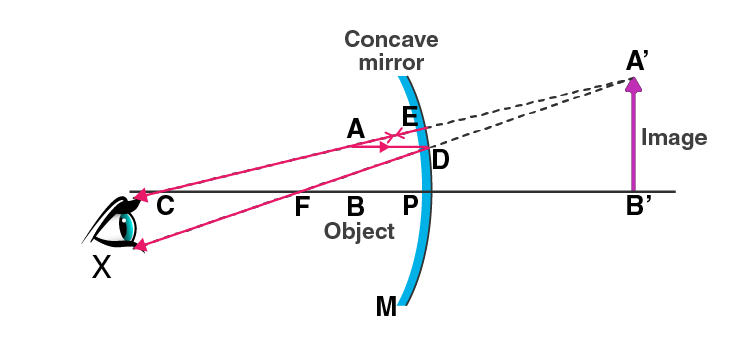
Q14. With the help of a ray diagram, determine the position, nature, and the size of the image formed of an object placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror.
Answer:
When an object is placed at the centre of curvature, C of a concave mirror, following is the image formed:
a) at the centre of curvature
b) real and inverted
c) the size of the image is equal to the size of an object
Q15. Describe with the help of a diagram, the nature, size, and the position of the image formed when an object is placed beyond the centre of curvature of a concave mirror.
Answer:
When an object is placed beyond the centre of curvature of a concave mirror, the image formed is:
a) between the focus and the centre of curvature
b) real and inverted
c) smaller than the object
Q16. If an object is placed at a distance of 8cm from a concave mirror of focal length 10cm, discuss the nature of the image formed by drawing the ray diagram.
Answer:
The focal length of the mirror, f = 10cm
The object is placed at = 8cm
Therefore, it can be said that the object is between the pole and the focus of the concave mirror
Therefore, the image formed is virtual, erect, and magnified.
Q17. Draw a ray diagram showing how a concave mirror can be used to produce a real, inverted, and diminished image of an object.
Answer:

Q18. Which mirror is used as torch reflector? Draw a labelled diagram to show how a torch reflector can be used to produce a parallel beam of light. Where is the bulb placed in relation to the torch reflector?
Answer:
Concave mirror is used for a torch reflector.
Q19. State where an object must be placed so that the image formed by a concave mirror is:
a) erect and virtual
b) at infinity
c) the same size as the object
Answer:
a) For erect and virtual, between the pole and the focus of the mirror
b) For infinity, at the focus of the mirror
c) For the same size as the object, at the centre of curvature of the mirror
Q20. With the help of a labelled ray diagram, describe how a converging mirror can be used to give an enlarged upright image of an object.
Answer:
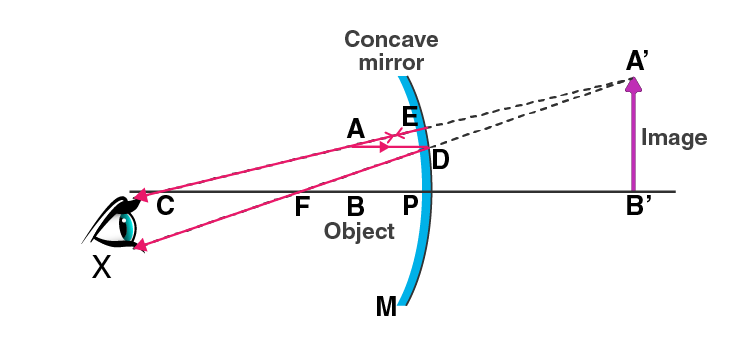
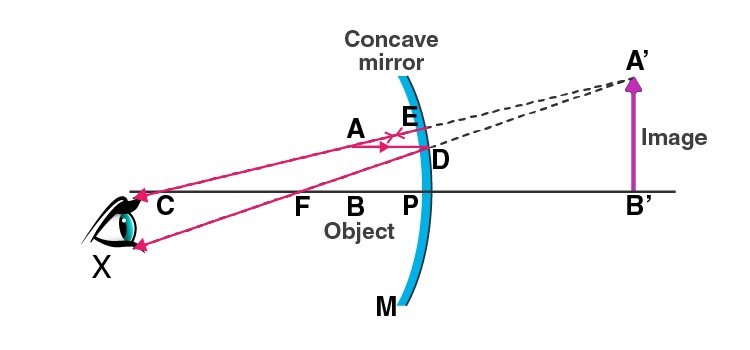
For obtaining an enlarged image which is upright, the object must be placed between the focus and the pole of the concave mirror.
In the diagram below, AD is drawn parallel to the principal axis such that D gets reflected and passes through the focus F. The second ray AE is passing through the centre of curvature striking at E and getting reflected back. DF and EC are the two diverging rays that do not intersect each other on the left side. DF and EC are produced backwards. When they are produced backward, they appear to intersect at the point A’. Therefore, A’ is the virtual image of point A. An enlarged image is obtained by A’B’ is drawn perpendicular to the axis.
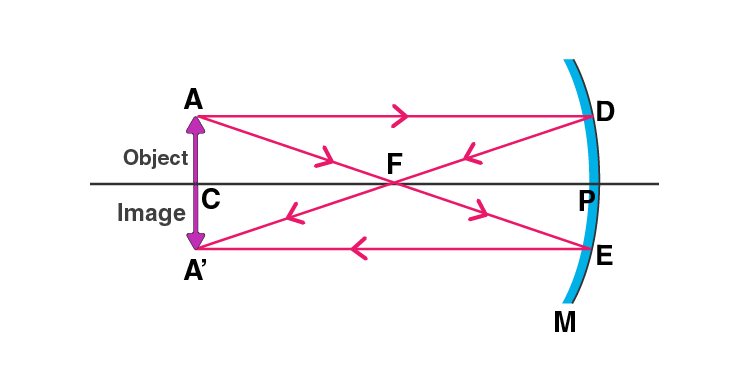
Q21. Make labelled ray diagrams to illustrate the formation of:
a) a real image by a converging mirror
b) a virtual image by a converging mirror
Mark clearly the pole, focus, centre of curvature, and the position of object in each case.
Answer:
a) A real image by a converging mirror
b) A virtual image by a converging mirror
Q22. Briefly describe how you would find the focal length of a concave mirror quickly but approximately.
Answer:
For determining the focal length of a concave mirror, the object should be placed a considerable distance from the concave mirror such that the image is formed at the focus. This is done by focusing a distant object such as a tree by using a concave mirror. A sharp image of the tree is formed at the focus of the concave mirror. Therefore, the distance of the image from the concave mirror will be equal to the focal length of the concave mirror.
Q23. Which type of mirror is used in a solar furnace? Support your answer with reason.
Answer:
A concave mirror is used in a solar furnace. The solar furnace is placed at the focus of a large concave reflector. When the light rays fall on the surface of the concave mirror, the rays get reflected and meet at the focus of the mirror due to the converging nature of the concave mirror resulting in the heating of the furnace.
Q24. Name the type of mirror used by dentists. How does it help?
Answer:
Dentist use a concave mirror. Dentist hold the concave mirror in such a way that the tooth lies within the focus. A magnified image of the tooth is seen by the dentist which helps them in examining the defects.
Q25. Explain why concave mirrors are used as shaving mirrors.
Answer:
Concave mirrors are used as a shaving mirrors because when the face is placed close to the mirror, a magnified image is obtained which is erect in nature. Thus helping in smoother shave.
Q26. Give two uses of concave mirrors. Explain why you would choose concave mirrors for these uses.
Answer:
Following are the uses of a concave mirrors:
a) Concave mirrors are used as a shaving mirror as a magnified and erect image is formed helping in smooth shave.
b) Concave mirrors are also used by the dentists as an enlarged image is obtained helping them in detecting the defects in the tooth.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q27. a) Draw ray-diagrams to show the formation of images when the object is placed in front of a concave mirror:
i) between its pole and focus
ii) between its centre of curvature and focus describe the nature, size, and position of the image formed in each case
b) State one use of concave mirror based on the formation of images as in case (z) above.
Answer:
a)
i) When the object is placed between the pole and the focus of a concave mirror, the image formed is behind the mirror and it is virtual, erect, and larger than the object.
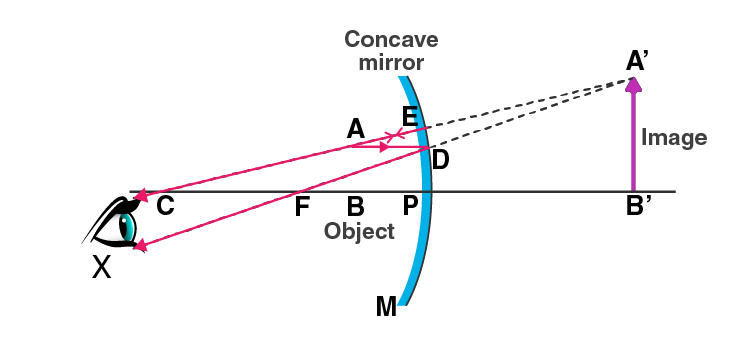
ii) When the object is placed between the centre of curvature and focus of a concave mirror, the image formed is beyond the centre of curvature. The image obtained is real, inverted, and larger than the object.
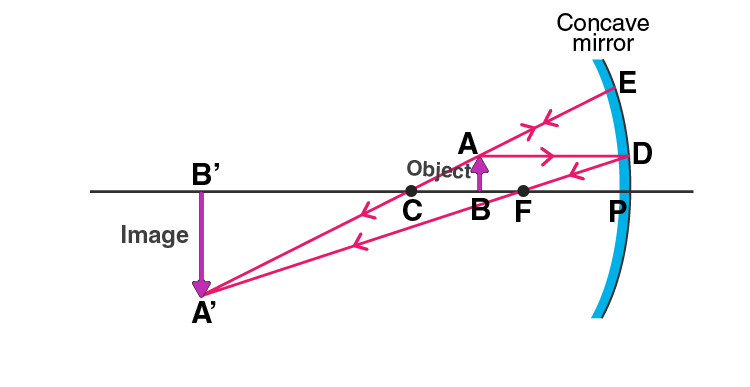
b) One use of concave mirror based on the formations of images is it is used as a shaving mirror.
Q28. a) Give two circumstances in which a concave mirror can form a magnified image of an object placed in front of it. Illustrate your answer by drawing labelled ray diagrams for both.
b) Which one of these circumstances enables a concave mirror to be used as shaving mirror?
Answer:
a)
i) When the object is placed between the pole and the focus of a concave mirror, a magnified image is formed.
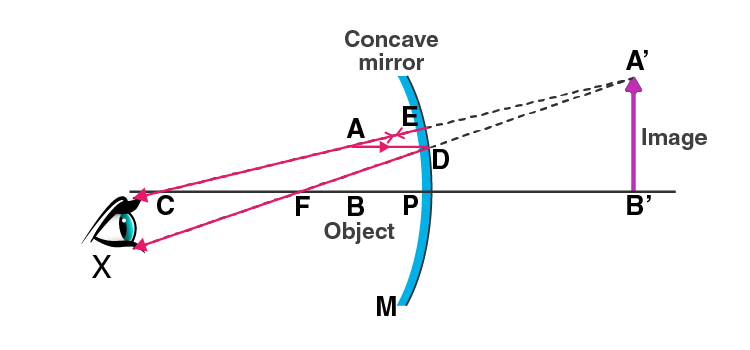
ii) When the object is placed between the focus and the centre of curvature of a concave mirror, a magnified image is formed.
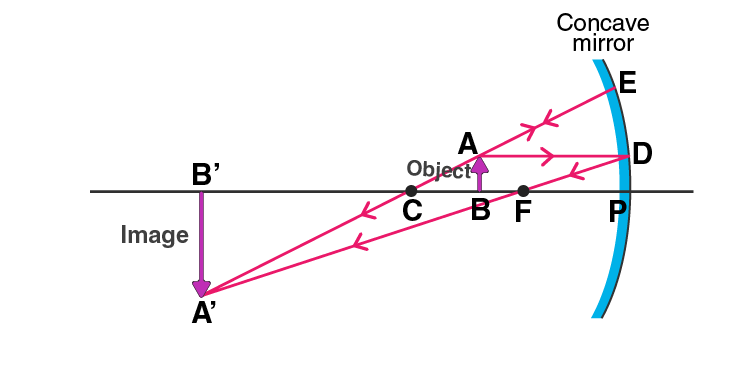
b) A concave mirror can be used as a shaving mirror when the object is placed between the pole and the focus of the concave mirror.
Multiple Choice Questions
Q29. The real image formed by a concave mirror is larger than the object when the object is:
a) at a distance equal to radius of curvature
b) at a distance less than the focal length
c) between focus and centre of curvature
d) at a distance greater than radius of curvature
Answer:
The correct option is c) between focus and centre of curvature
Q30. The real image formed by a concave mirror is smaller than the object if the object is:
a) between centre of curvature and focus
b) at a distance greater than radius of curvature
c) at a distance equal to radius of curvature
d) at a distance equal to focal length
Answer:
The correct option is b) at a distance greater than radius of curvature
Q31. The image formed by a concave mirror is virtual, erect, and magnitude. The position of object is:
a) at focus
b) between focus and centre of curvature
c) at pole
d) between pole and focus
Answer:
The correct option is d) between pole and focus
Q32. The image formed by a concave mirror is real, inverted, and of the same size as the object. The position of the object must then be:
a) at the focus
b) between the centre of curvature and focus
c) at the centre of curvature
d) beyond the centre of curvature
Answer:
The correct option is c) at the centre of curvature
Q33. The image formed by a concave mirror is real, inverted, and highly diminished (much smaller than the object). The object must be:
a) between pole and focus
b) at focus
c) at the centre of curvature
d) at infinity
Answer:
The correct option is d) at infinity
Q34. The angle of incidence for a ray of light passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror is:
a) 45 degree
b) 90 degree
c) 0 degree
d) 180 degree
Answer:
The correct option is c) 0 degree
Q35. In the concave reflector of a torch, the bulb is placed:
a) between the pole and focus of reflector
b) at the focus of reflector
c) between focus and centre of curvature of reflector
d) at the centre of curvature of reflector
Answer:
The correct option is b) at the focus of reflector
Q36. The focal length of a small concave mirror is 2.5cm. In order to use this concave mirror as a dentist’s mirror, the distance of tooth from the mirror should be:
a) 2.5cm
b) 1.5cm
c) 4.5cm
d) 3.5cm
Answer:
The correct option is b) 1.5cm
Comments
Post a Comment